How to create an effective Customer Journey Map: Complete guide to improving User Experience
In today’s digital world, optimizing user experience (UX) is crucial for the success of any business. A key tool to achieve this goal is the Customer Journey Map. This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to create an effective Customer Journey Map, from basic concepts to practical examples and case studies.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) is a visual representation of the path a user takes while interacting with a brand. This map helps companies better understand the emotions, needs, and pain points of their customers at each stage of the buying process, providing a comprehensive view of their experience.
Benefits of a Customer Journey Map
- Empathy: Helps employees put themselves in the customers’ shoes and better understand their perspectives.
- Pain Point Identification: Allows the detection of barriers in the buying process, helping to improve the overall experience.
- Continuous Improvement: Facilitates the identification of areas for improvement to continuously optimize the customer journey.
- Resource Optimization: Enables more efficient allocation of resources and efforts by focusing on areas that directly impact the customer experience.
Differences between Customer Journey and User Journey
A common question is: What are the differences between Customer Journey and User Journey?
- Customer Journey: Focuses on the complete path of the customer, from the first contact with the brand to post-purchase and retention. It includes all interactions and experiences the customer has with the company over time.
- User Journey: Focuses on the specific experience of the user with a digital product or service, such as an app or website. It is more detailed regarding user interactions with the interface and product functionalities.
Both concepts are important and often overlap. However, the Customer Journey covers all interactions with the brand, while the User Journey focuses on the specific digital experience.
Steps to create an effective Customer Journey Map
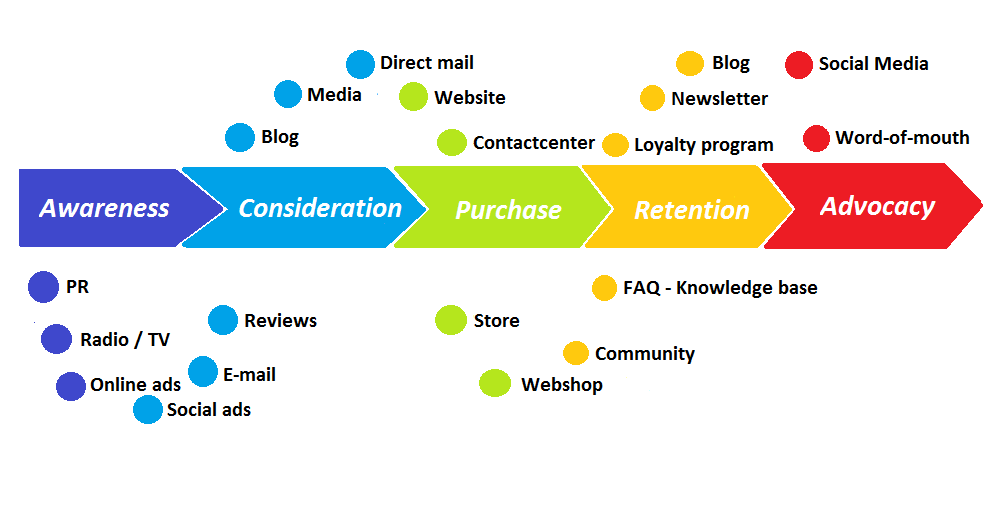
-
Research and Define Your Users
The first step is to understand who your users are. Conduct surveys, interviews, and analyze demographic and behavioral data to get a clear view.
Practical Example: If you manage an online clothing store, you might identify “Laura,” a 30-year-old woman looking for trendy clothes at affordable prices.
2- Identify the Stages of the Customer Journey
The stages of the customer journey vary by business type, but generally include:
-
Discovery: The user discovers your brand.
- Consideration: Investigates and compares your products or services.
- Decision: Decides to make the purchase.
- Retention: Post-purchase interactions to foster loyalty.
-
Advocacy/Promotion: The satisfied customer recommends your brand to others, becoming a brand advocate.
3- Map the Touchpoints
Identify all the touchpoints a user has with your brand at each stage of the customer journey.
Practical Example: For “Laura,” touchpoints might include searching on Google, visiting social media, browsing the website, and receiving post-purchase follow-up emails.
4-Analyze emotions and needs
At each touchpoint, understand the emotions and needs of the users.
Practical Example: During the “Consideration” stage, Laura might feel excited seeing a special offer but frustrated if the checkout process is complicated.
Tools for creating a Customer Journey Map
- Google Analytics: To analyze user behavior on your website.
- Miro: An online collaboration tool ideal for creating visual maps.
- Smaply: For designing and personalizing CJMs effectively.
- UXPressia: Offers specific templates for CJMs and detailed analysis.
Case Studies
-
Payment Process Improvement at ASOS
ASOS, one of the leading online fashion retailers, experienced a high cart abandonment rate during checkout. By conducting a detailed customer journey analysis, they identified that the process was too complicated and lengthy. They simplified the payment process, integrated faster payment options, and improved navigation. As a result, they saw a 20% reduction in cart abandonment rate and a 15% increase in conversions.
-
Customer Service Optimization at Slack
Slack, a team messaging platform, found that new users faced difficulties during the initial setup process, affecting their experience and satisfaction. By mapping the customer journey, they identified critical points and frustration areas. They implemented interactive tutorials, help videos, and real-time support. These improvements led to a 30% increase in user retention during the first three months and a significant decrease in support tickets.
Creating a Customer Journey Map is not just a UX tool; it is an essential strategy for any company that wants to improve user experience and build customer loyalty. By following these steps, you will better understand your users, optimize their experience, and ultimately build stronger and longer-lasting relationships with them.
Remember: A Customer Journey Map is not a static document, it’s a living tool that should be reviewed and updated regularly. Observe how your customers interact with your product or service and adjust your map accordingly.
I hope this article has been helpful!




